Pharmacy Disruption: an interview with Zottii
Taz Sheikh is CEO of medicine delivery start-up Zottii. He talks to Curzon Consulting about pharmacy disruption, the impact of COVID-19 and future of pharmacies.
The gap in medicine delivery models for retail pharmacies has been exacerbated by Coronavirus, increased demand and changing customer expectations.
Interview with Taz Sheikh, CEO of Zottii
We live in a day and age where we can get almost anything delivered on demand and on the same day, whether it be items on Amazon, to your groceries to take-away food or taxis. So you’d think the same will be the case when it comes to prescription medicines, but sadly is not. So in early 2019, I set about looking at ways to change that.
I really thought that there’s got to be a better way a better experience for me as a potential patient, for doctors and for the whole healthcare system as a whole.
And hence I decided to create Zottii.
Challenges in retail pharmacy
-
It’s behind the times. And it’s not really set up for those people who need their medications in a hurry, or who physically cannot get to a pharmacy
-
It’s inconvenient. You know we all live very busy lives today. So find the time to visit a pharmacy, it’s not ideal, you know, particularly if you’re a busy working professional like yourselves, or you’re a single parent or you’re, you have young children
-
The biggest problem right now within retail pharmacies is the out-of-stock situation, it’s common for pharmacies to be out-of-stock of your particular medication 40% of the time. Most do not have the appropriate inventory systems to ensure a continuous supply of the right medications
-
This out-of-stock situation leads to something what we called poor drug compliance. And the inability of people being able to get their medications when they need which often leads them to not actually taking their medications at all. And this potentially causes further problems, not only for the patient, but also for the whole healthcare system as a whole as delayed treatment ultimately does result in worse outcomes.
-
Most pharmacies are just not set up to offer on-demand or same day delivery, and those that do somehow offer that service, quite often it’s complicated as it involves third party couriers, and it can be quite costly. The current suite of online pharmacies use the Royal Mail [UK’s postal service], which often means patients have to wait 2-5 days to receive their medications
-
[Retail pharmacies] are really designed to get people to the door because they’re selling makeup shower gels, toiletries. And most shelves are used up to stock those particular items. And if you actually look at their actual dispensary of prescription medicines, often is a very small space, they don’t always have the space to stock all the inventory
Benefits of online medicine delivery
Opportunity for pharmacy disruption
If new disruptors do not come into this sector and use technology to be able to streamline the whole process it will create more of a burden in the future, not only for patients and for doctors but for the whole healthcare system as a whole.
You’ve had many people look at the front end of healthcare, the likes of these very prominent video consultation platforms. Some of these platforms use AI technology but sometimes people forget about the most crucial element, you still need to get the medicines that are being prescribed into the patient’s hands. It doesn’t matter how many remote consultation platforms you have out there. If people are still not getting their medicines it means nothing.
Evolving customer expectations
We want to bring pharmacy as it is into the current time and we wanted to be a service that’s more aligned with consumer expectations today, as in getting your medications delivered on demand on the same day to a time and place or location that suits you.
The other thing is that we’re trying to make it more convenient.
Ultimately, our service is really designed to help those who need the service get their medications in a timely fashion. Whether you be elderly, single parent, busy working professional, or whether you be someone who’s incredibly tech savvy.
We’re already seeing a younger generation who are basically choosing healthcare on their own terms. They’re using services like video consultations, or chat enabled AI systems. All those systems lend themselves very well to a delivery service such as what we’re offering. It’s completely plausible to expect to have your medications delivered to your home if you’re having a video consultation with your doctor at home.
Predictive software
The reason we are also trying to avoid that no-stock situation is because we’re employing certain types of predictive inventory software and we’re looking at the data around what medications are most consumed. And we also look at the most commonly prescribed drugs of a doctor who uses our service to always ensure that we have an adequate supply.
Faster treatment
By offering free same day delivery, often within one to three hours, we’re quite setup for those people who’ve got time critical care needs. We’re helping people get treated faster, which results in better drug compliance, which results in better medicine adherence.
Continuity of care
Doctors love the service because not only can they send their prescription to us electronically but they also are notified the moment deliveries made so from a continuity of care point of view. And it’s also a value added service for them because as it stands today there’s a detachment from pharmacy and doctor.
Your doctor doesn’t know the challenges that you’re going to face as a patient to try to get your medication. They don’t even know necessarily if you’re going to take your medication because of the fact that you can’t get it, but with a service like AWS they have the comfort knowing that we’ve received their prescription.
Impact of COVID-19
The Coronavirus pandemic has seen the acceleration of digital transformation for many industries, including pharmacy disruption. We discuss the long term impact of the change in behaviour and customer expectations exacerbated by COVID-19.
Increase in demand
The demand for our services absolutely has gone through the roof.
We were originally delivering in (London) zones one to four. We have now stretched out to zones one to six.
Change in operations
What I’ve noticed over the past few weeks with the current COVID-19 lockdown is that a number of the pharmaceutical wholesalers have had to really streamline their delivery services.
Our delivery drivers have obviously had to change the way they operate and work within this current lockdown situation. We’ve had to focus purely on online payments.
Change in mindset
People don’t want to go out and pick up the medicine because they don’t want to risk exposing themselves to other people. And if anything, this whole pandemic really hits home two key things:
- Sick people shouldn’t have to go to the pharmacy. When you’re unwell you can get anything else delivered to your home… Why should you not get your medicines delivered to you?
- Sick people shouldn’t be going out in public: They shouldn’t be going to the pharmacy risking exposure to the pharmacist, they shouldn’t be using public transportation risking exposure to other people. They should stay at home and let services, such as Zotti or similar, come and deliver their medicines to them at home.
Future of Pharmacies
The role of robotics
By the year 2050 the majority of dispensaries will have some form of robotic dispensing capability because:
- they can operate 24/7
- they can be linked to whatever system they need to be. They can be linked directly to a doctor’s prescribing platform
- the use of AI technology can also be in place to minimise any mistakes doctors may make
I think it’s a given pharmacy of the future will be more tech enabled, it will be more integrated and they will be a logistics element attached to the end of it.
The value chain
In terms of the whole ecosystem, I think a more integrated and more thorough pharmacy element is definitely required, certainly in terms of dealing with not only primary care patients but secondary care patients as well. A service such as what we offer does not have to be just focused on prescription medication. We could also be delivering Over the Counter (OTC) products and other products you would typically get in the pharmacy. We already know what the most popular Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) are within the pharmacy. And if you’re delivering medications to a particular individual, why not also deliver the other types of products that they would traditionally get from their pharmacy?
Pharmacists of the future
I think the reality is that there will always be a place for pharmacists… technology will not completely replace the need for a superintendent pharmacist.
But I think the question is who will they work for. There certainly will be in the future options to work for some of these technology disruptors within this space or the ability to embrace technology in their own pharmacy.
I think the industry as a whole needs to give more powers to pharmacists. We’re already seeing more and more pharmacists, with the ability to prescribe. And I think that will start to increase.
Is retail pharmacy ready for disruption?
Curzon Consulting helps organisations with digital strategy and transformation. If you would like to discuss how a multi-channel strategy could be implemented into your current business model, get in touch.
Contact us for more information or submit a request for proposal to our healthcare consulting team
Touchless Travel: automation in airports post COVID-19
Automation in airports may enable touchless travel. The global COVID-19 pandemic has caused widespread disruption around the world and brought with it a lot of uncertainty. The response from many healthcare systems and technology companies highlights the increased adoption of digital tools and innovative solutions.
Curzon Consulting Partner Chetan Trivedi interviews innovators in the UK healthcare sector. In his latest conversation, Chetan explores automation in airports post COVID-19.
Bob Kwik, Director Europe at Elenium Automation, a passenger experience company focused on improving the journey using automation and technology.
The company is also working with hospitals to roll-out self-service triage solutions. Etihad Airways recently announced that it plans to partner with Elenium Automation to trial new technology which allows self-service devices at airports. The technology will be used to help identify travellers with medical conditions, potentially including the early stages of COVID-19. Etihad will initially trial the monitoring technology at its hub airport in Abu Dhabi in May and June 2020.
Get in touch to discuss how digital strategy and transformation can be applied in your organisation.
Contact us for more information or submit a request for proposal to our healthcare consulting team
Remote working during COVID-19 - "Kudos is better than caffeine"
In his first blog post, senior consultant Phil Hanson explores seven lessons he learned in the army that can be applied to remote working during COVID-19.

Image courtesy of Johnny Fenn Photography
People naturally avoid difficult conversations
Ten years in the Army taught me more than I could possibly convey in a single thought leadership piece. However, some of my experience, including front-line combat in Afghanistan, left me some unique insights into team dynamics and leadership in extreme circumstances, many of them pertinent to the COVID-19 pandemic. The seven lessons I learned during my Army career I feel most useful for thriving under difficult conditions are:
Everyone responds differently to stress, and that’s OK
Like infectious diseases, stress responses have a lag time which can vary enormously by individual. This means treating people with patience, followed-up with a bit more patience.
Personality is a poor predictor of stress-response; I have witnessed shy, retiring individuals quietly carrying teams through astonishing adversity. The only consistent truth is that the appropriate response involves patience, compassion and understanding.
Consider the most candid conversation you’ve ever had; someone truly opening up to you about something personal. Now reflect on how it began. It probably meandered through small-talk before finally settling on the real issue once they felt comfortable enough to raise it.
Remote-working makes it too easy to close conversations early. Give people your time, make them feel valued and listened to: Make difficult conversations that bit easier.
Trust is not optional in high-performing teams
It’s often said that what sets the British Army apart is the quality of its Non-Commissioned Officers: Highly-trained, empowered junior mangers who are told what to achieve, not how to achieve it, in a concept known as Mission Command. This reciprocal-trust environment brings out best of the team’s collective strengths.
Virtually everyone responds best to a default position of trust; and will strive to justify this faith placed in them. The rare exceptions to this rule are rapidly exposed, rendering the concept of “respect is earned” redundant in the modern consulting profession.
Professionalism is a mindset
In 2015 my Battalion received new Colours from the Queen: The parade was the culmination of months of painstaking rehearsals and uniform preparation. The result of this was that on the day, leathers polished and medals shining, I felt utterly prepared to perform in front of 20,000 people. Equally, I would never deploy on operations without every bit of my kit being just-so. Both scenarios boil down to one principle: Being every-inch the professional soldier.
Wearing pyjamas whilst WFH every other Friday may be an understandable novelty, but long-term, looking and feeling in work-mode is critical to working in work-mode. It also helps delineate work-life balance.
You have to look after yourself in order to take care of others
Being an infantry officer often involves rapid decision-making whilst exhausted, soaking wet, and freezing cold. Typically, this means making personal sacrifices for the sake of your soldiers, but a good leader knows they need to take sufficient care of themselves to make the right tactical decisions.
It’s too easy to neglect ourselves, convinced we’re doing right by colleagues, friends and family. Granted it’s a tricky balance to strike, but the longer difficult scenarios last, the more important it is to take care of ourselves too. It’s what’s best for the whole team.
Followership is just as important as leadership
Despite all knowing that too many cooks spoil the broth, when we analyse team dynamics, we too often focus exclusively on leadership qualities at the expense of others.
Whether you call it followership, or just being a team player, the art of knowing your role, doing it to the best of your ability and supporting leaders is an often-overlooked critical success factor for high-performing teams.
Kudos is better than caffeine
Whilst it may not exactly be ground-breaking news, it’s nonetheless true that most people could be better at giving credit to others. When the going gets tough, it’s easier than ever to forget to say well-done, despite it being more important than ever.
Coffee may flow through the veins of many consultants, but recognition for job well-done provides a boost that is far more enduring than a caffeine fix.
CONTACT US TO FIND OUT HOW WE CAN HELP
Virtual Care: delivering healthcare in the new reality
The global COVID-19 pandemic has caused widespread disruption around the world and brought with it a lot of uncertainty. The response from many healthcare systems is showing the increased adoption of digital tools and innovative solutions.
Whilst Virtual Care services are nothing new, the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed Virtual Care solutions like Telehealth to the top of the healthcare agenda. In order to deal with increased demand for healthcare services, governments around the world have pushed through regulatory changes to allow the widespread use of Virtual Care models. These Virtual Care platforms are an indispensable tool in an environment where health systems try to keep up supply (clinical assessments and triage) with demand (patients).
In a post COVID-19 world, care delivery models around the world will be transformed and there will be widespread adoption of Virtual Care models in virtually every healthcare setting. This is part of a wider digital transformation agenda in healthcare. Care that used to take place exclusively in physical settings (e.g Doctor’s office) can now take place digitally. Every healthcare organisation (payors, hospitals, life sciences, pharma, medical devices etc.) across the entire value chain (prevention, primary care, secondary care, tertiary care, social care, palliative care, etc.) are exploring a variety of virtual care models, many of which are enabled by telehealth technology.
Hospitals are already using Virtual Care to improve accessibility, availability and affordability of care. As demands for healthcare services increase, driven by an aging population requiring more complex care, Virtual Care offers a smart way to leverage finite healthcare resources.
Virtual Care and digital healthcare enable a model of care that is more affordable and integrated into patients’ lives. Consumer behaviour is also shifting. As Dr. Eric Topol describes in his book titled “The Patient Will See You Now”, patients seek to access healthcare on their own terms (time and place).
Hospitals and health systems that take a proactive approach towards Virtual Care will be well-positioned to meet patient demands in the future.

Definitions
Virtual care is comprised of four categories:
Real-time interaction with the most appropriate clinical team to support patient requiring immediate advice. Post virtual triage, a follow face-to-face consultation with the most appropriate clinician team (doctor, nurse, pharmacist, etc.) can take place.
Modern information and communication technologies, data such as bio-signals or medical images can be acquired from the patient and then stored or sent to the specialist when needed. The field of Pathology, Radiology, and Dermatology are those using such services already. For example, with a shortage of Radiologists in certain countries, scans can be read and reported on by specialists remotely. If Artificial Intelligence (AI) is layered on top, certain scans can be read by AI to act as a “second pair of eyes” to human reads.
Uses a range of technological devices in order to remotely monitor clinical signs and health of a patient. Remote monitoring is extensively used in the management of chronic diseases such as asthma, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 6 in 10 adult Americans live with at least one chronic disease and 4 in 10 adults live with two or more chronic diseases. Among the benefits of virtual care include greater patient satisfaction, more frequent monitoring, and cost effectiveness.
There is a strong tendency that patients are involving more in monitoring their own health through the use of smartphone applications and wearable devices designed to help them track and improve various health indicators.
According to Statista, there are 3.2 billion smart phone users out of a total population of 7.7 billion people around the world. This information and these devices can be also used by policymakers, practitioners, and leaders in the medical and health care industry in order to identify and act on health trends, inform treatment decisions, and even provide outgoing communication to the public.
Such solutions can also deliver basic care to parts of the population living in remote locations. For example, nutrition advice can be provided remotely to pregnant women and/or mothers with young children in small villages with virtually no access to care, but may have access to mobile technology.

“Use” cases
By increasing access points and redistributing expertise where it’s needed, Virtual Care can address disparities and improve outcomes. Virtual Care platforms can be used to provide a range of services such as, but not limited to:
Primary Care
- Chronic care management, recording vital signs through home-monitoring systems and sending alerts to clinicians when readings fall out of the normal range.
- Pharmacy services, including medication review and prescription verification, for patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, etc.
- Diagnostic screening for diabetes-related eye disease, increasing the number of diabetes patients who receive eye exams to help prevent blindness.
- Sleep disorders, monitoring patients with sleep apnoea for sleep patterns, body positions and breathing.
- Tele-psychiatry, assisting patients in need of behavioural health services.
- Tele-physiotherapy, assisting patients with physiotherapy sessions remotely.
Acute/Hyper-Acute
- Tele-stroke services, creating access to the limited supply of stroke neurologists and targeted use of therapies that preserve brain function and save lives. Tele-stroke services can also help facilitate a “hub and spoke” model, where a hyper-acuity stroke unit can provide remote support to a stroke centre.
- Tele-ICU tools, providing 24-hour intensive support to deliver optimal local care to the most acute patients. ICU beds can all be monitored from one, central control room anywhere in the world.
- Pre & Post Op Consultations, ensuring more efficient use of resources across the health system where a physical exam on the day is not required. For example, a patient scheduled for a cardiac ablation procedure can be consulted remotely prior to the procedure, once certain tests have been performed in advance.
- Post-surgical recovery, allowing patients to self-manage recovery process with support from clinical teams as needed remotely. Sophisticated solutions can also include apps to capture progressive pain scores, wound images, etc. so that clinical teams can monitor recovery remotely.

Adoption Challenges
There are some barriers to expanding access to care through Virtual Care. The eight most significant barriers are:
- The lack of leadership and organisational commitment to develop an overarching strategy and integrate care delivery within the clinical pathway (e.g. pre and post op consultation)
- Inadequate clinical engagement and readiness without consideration of user (clinicians and patients) experience and workflows
- Restrictions on how Virtual Care services are reimbursed
- Licensure laws and regulations that limit the ability to provide Virtual Care services across multiple jurisdictions (i.e. from one state to another within the US)
- The lack of “connectivity” or adequate internet services in some areas to support Virtual Care
- Decentralised departmental solutions and pilot programs without governance structure and dedicated management and potentially competing propositions
- The high cost of technologies and infrastructure and a lack of funding
- Evolving measures of success and key performance indicators hampering scaled platforms
As a result of COVID-19, many of these hurdles are being taken down rapidly to help drive quicker adoption of Virtual Care services.

Key Success Factors
How do hospitals and health systems begin to harness the benefits of Virtual Care?
Virtual Care is not about technology. Technology is simply an enabler! It starts with culture—and culture starts with the Board and Executive Management team. The governing board and senior management can ignite cultural change with a vision statement that embraces virtual care as an extension of what the hospital or health system already does, rather than as something new or different.
Successful hospital and health system Virtual Care programs require discerning technology choices and critical vendor selection. Success also demands uncomfortable cultural changes and the right executive to create a comprehensive virtual care delivery system for patients.
We can help your organisation develop a business case for virtual care. We can help you redesign clinical pathways so that virtual care is not a standalone model, but is truly integrated into the delivery of patient care along the entire pathway.
Contact us for more information or submit a request for proposal to our healthcare consulting team
Future of Infrastructure 2020 report
This 2020 report by Raconteur explores the future of infrastructure, including:
- Smart cities, digital and new technologies
- Sustainability and the challenge of achieving net-zero
- Public perceptions of infrastructure in G8 countries
- Future-proofing infrastructure against climate risks
- Reusing existing assets to bring buildings into the circular economy

How we can help infrastructure organisations
At Curzon Consulting, we understand it’s about the destination and the journey.
We work with rail, road and utilities organisations to deliver tangible results. Our award winning management consultants help our clients get where they need to be through:
- Digital Monetisation and Transformation
- Data Driven Decision Making
- Operating Model Future Proofing
- Value Enhancing Strategies
Visit our infrastructure page or contact our Infrastructure Lead, Nigel Brannan, to find out more
Download ‘Future of Infrastructure 2020’ report from Raconteur, The Times
Related articles
Nothing found.
CONTACT US TO FIND OUT HOW WE CAN HELP
Forming the new organisation around purpose
Managing Consultant Rodrigo Quezada Dighero attends Working Futures on 13 November 2019. At this event, they’ll be discussing the challenges HR Directors need to overcome to deliver greater productivity, digital transformation and formalise new strategies around organisation purpose.
HR's changing role
HR’s role now is to deliver the performance, frameworks and environments for both people and systems to allow true business transformation. This requires HR to reorganise itself and to grasp the purpose of the organisation and formalise new strategies around the purpose of the company.
We’ll be attending Working Futures on the 13th November 2019. There we will debate these elements and provide the shift in thinking that HR Directors now need to form the productive organisation.
Challenges organisations face
- Disruptive technologies
- Low entry barriers, new segments served
- Short product lifecycles
- Stress, wider product portfolio, product profitability
- More demanding customer experience
- Customer service, customer journey and customer lifecycle
- Multi-generation workforce – there are now 5 generations in the workforce
The challenges leaders face is how to envision, set and lead a flexible organisation that can quickly adapt and thrive in an ever changing and demanding environment
Creating a flexible and meaningful organisation requires a different approach
Forming strategy around purpose
Purpose:
- Allows peers and management to set a connection towards something bigger than just business profits
- Enables a multi-generation workforce to connect around a greater outcome
- Encourages disruptive design and thinking
- Allows the company to adapt, move and thrive by creating the products and services that best serve clients
- Facilitates flexibility to respond rapidly
- Provides speed to execution and calibration
- Allows people and teams to risk and innovate
- Eliminates silos, fostering interdependence, trust and team work
Many high-growth companies use purpose to generate sustained profitable growth, stay relevant in a rapidly changing world, and deepen ties with their stakeholders.
Targets and incentive plans became cross-functional, designed to build capabilities both within and across businesses. And at every step, purpose helps everybody in the company understand the “why”.
Questions leaders can ask about their organisation
Leaders need to constantly assess and calibrate how purpose can guide strategy, and they need to be willing to adjust or redefine this relationship as conditions change. Questions Leaders and People/HR Directors should be asking are:
- Does your company have a purpose?
- Do your company have a clear vision?
- What drives your company’s vision?
- Is your vision based on a clear purpose?
- Are your plans and projects tightly connected to your purpose and business outcomes?
- Are your people aligned around your vision?
How we can help HR Directors to align the organisation around purpose
- “From There To Here” Design
- Transformational maps
- Pathways definition
- Disruptive design
- Interdependence and shared outcomes
- Identifying Blockers and gaps
- Identifying Behaviours
- Putting in place new structures
In addition, we can help HR Directors with
- Strategic Workforce planning
- Digital Transformation
- HR Transformation
- Change management
- Recruitment Excellence – readiness assessment and implementation
- Culture
- People
- HR Target Operating Model
- HR Processes
- HR Supplier Management
- HR Rewards
- Talent Acquisition and Management
- Performance Management
- HR ITS and Applications (WorkDay, SAP HCM, Oracle HCM)
- Programme and Implementation Support
Get in touch to find out how we can help your organisation with strategy, digital and HR transformation.
CONTACT US TO FIND OUT HOW WE CAN HELP
Healthcare change: a perfect storm is brewing
Curzon Consulting Healthcare lead, Chetan Trivedi, argues that a perfect storm is approaching in Healthcare, and it’s been brewing for a while…
On one hand, we are seeing an ageing population, with growing multiple comorbidities, requiring more complex care. On the other hand, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), in 2017, global debt had reached an all-time high of $184 trillion in nominal terms, the equivalent of 225 percent of GDP.
In order to “move the needle”, Healthcare systems need to radically move away from “tinkering round the edges”, and instead, focus on delivering transformative change (focusing on prevention, implementing new care delivery models enabled by technology, better triaging and stratifying patients to determine best intervention point (hospital, community, home, etc.), leveraging appropriate skills set to treat patient (physician versus pharmacists versus nurse, etc.).
Some of the choices may not be popular, but if left unchecked, on the current trajectory, we will leave the future generation with a formidable challenge.
So, what are the 10 factors generating the perfect storm in healthcare?
1. Economic headwinds
Unprecedented level of total global debt-to-GDP (225%)* during peace time. Simply printing more money, creating more debt or throwing more funds at an outdated healthcare system is not going to help. Health systems need to improve quality and reduce cost-per-capita quickly. Focus on evidence-based disease prevention is key.
*Global debt has reached an all-time high of $184 trillion in nominal terms, the equivalent of 225 percent of GDP in 2017. On average, the world’s debt now exceeds $86,000 in per capita terms, which is more than 2½ times the average income per-capita. International Monetary Fund, 2019
2. Demographic time-bomb
An aging population with multiple comorbidities is requiring more complex care, so healthcare patients need to be better triaged and stratified to determine the best intervention point (hospital, community, home, etc.). The global population aged >60 years numbered 962 million in 2017, more than twice as large as it was in 1980. This figure is expected to double by 2050.**
3. Disease burden proliferation
We are seeing an increased prevalence of long-term chronic conditions such as hypertension and Type 2 diabetes. These are likely to add pressure on primary and secondary care organisations. Healthcare systems need to radically re-think “healthcare” with a greater focus on prevention and alternative care models such as community, home; GP vs. Pharmacist vs. Nurse.
4. Capacity constraints
The overcrowding of hospitals and emergency departments by patients who can been seen outside of the acute setting are causing delays for patients with higher levels of acuity to be seen earlier. Healthcare patients need to be better educated, triaged and stratified to determine the best intervention point (hospital, community, home, etc.).
5. Regulatory changes
Regulators are increasingly playing catch up with a fast paced, rapidly evolving healthcare sector, particularly with respect to innovation and technology. Commissioners are also pushing for greater cost transparency across the entire healthcare sector (i.e. hospital and drug pricing in the US, diagnostic and drug pricing in India, etc.)
6. Technology disruption
Rapid advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain, Genomics, Telehealth, Remote Monitoring technologies and customised medicines are allowing clinicians to deliver precision healthcare, whilst improving patient experience and lowering cost. Innovation promises to deliver speed, quality and productivity at scale and lower cost.
7. Patient expectations
Consumer expectations are rapidly rising. Younger patients are increasingly seeking to access care on their terms. The Patient-Doctor relationship is being transformed (“The Patient Will See You Now”***). Older patients are expecting far greater quality of life until much later in life, placing a major strain on healthcare systems such as orthopaedics and physiotherapy.
***The Patient Will See You Now, authored by American cardiologist, geneticist, and digital medicine researcher, Eric Topol
8. Healthcare model transformation
There is increasing pressure to develop high quality, less-expensive alternatives to traditional hospital care models. Increasing focus on delivering care in the community and patient’s home. Move towards Integrated Care, Value Based Outcome, etc. models to drive convenience, improved quality and aligned incentives (payers vs. provider).
9. Challenging treatment protocols
Pressure from patients and clinicians to challenge existing disease treatment protocols. For example, healthcare patients with long term chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes experimenting with low-carb diets to stop and reverse disease. Focus on prevention through life style changes.
10. Healthcare data explosion
An exponential increase in electronic data is being generated across the Healthcare continuum. AI and connected medical devices will take data generation and storage requirements to a scale not seen before. Securing all this data (on potentially a Blockchain) will be a leading priority for all stakeholders across healthcare.
Sign up to receive future healthcare insights to your inbox.
Chetan Trivedi
I lead Healthcare at Curzon Consulting.
For over 15 years I have supported Healthcare payers, providers and medical devices companies on strategy, operational improvement and digital transformation engagements across the UK, wider Europe, Middle East, US, India and Canada.
I am deeply passionate about improving health outcomes, safety and quality of life for patients.
Contact us for more information or submit a request for proposal to our healthcare consulting team
Digital transformation across UK infrastructure
Curzon Consulting have partnered with Victoria Trukhanovich to deliver an MBA research project at Cass Business School, on the topic of digital transformation.
Over a series of articles we will explore existing challenges, business requirements, relevant technologies and strategy that needs to be applied by infrastructure organisations in order to design and perform transformative digital change successfully.
In this introductory piece we present a summary of findings on the current state of digital adoption across the infrastructure industry, including the transport, utilities and construction sectors.
Using digital transformation to address challenges
The challenges that companies operating physical infrastructure face include:
-
- aging assets
- frequent incidents of underperformance
- capacity congestion
- inefficient capital and maintenance programmes,
- strong regulations
- dissatisfied customers
Digital transformation is increasingly viewed as an enabler to address these issues, providing opportunities for infrastructure companies to achieve significant gains in areas of system resilience, capacity utilisation, asset productivity, process efficiency and customer engagement.
Lagging digital maturity
Yet, the digital maturity of infrastructure companies lags behind that of many other industries. Although level of maturity varies across and within sectors, the majority of infrastructure companies have not started to implement digital technologies on a wide scale and digital activities are fragmented. Due to a number of legacy factors, infrastructure companies often lack the capacity to build a clear digital vision and drive technological change throughout the organisation.
Empirical evidence from digital transformation projects, conducted by Curzon Consulting with UK transport infrastructure network owners, water and sewerage companies and airport operators, reveals the common challenge of an inconsistent approach to digital integration. Companies often run innovative, technology-enabled initiatives on a project-by-project basis without systematically integrating technologies in line with strategic objectives.
The digital transformation strategy challenge
A dispersed digital agenda was thus found to be the most pressing challenge for companies to solve in order to assert direction within the transformation process and consolidate digital initiatives around achieving clear business objectives.
This study asks how infrastructure companies should go about developing an effective digital transformation strategy. The urgency of addressing this challenge is exacerbated for companies in competitive markets as digital leaders and emerging start-ups are well positioned to identify adjacent niches and secure dominant shares quickly.
The role of technology
To offer a summary of digital strategy recommendations, we seek to:
- assess the potential of critical digital technologies to deliver industry objectives
- identify key capabilities enabled by technological advancements
- examine the evolutionary timeline of digital transformation
- analyse organisational functions affected and value outcomes generated
Developing a framework for successful digital transformation delivery
Once developed and agreed at the corporate level a digital strategy framework can be used by infrastructure companies to evolve from an ‘adapting- enterprise systems’ approach into a smart network operator approach. Although each digital transformation programme will have a degree of uniqueness, the framework developed within this study offers a high-level plan for successful development and delivery of digital change in infrastructure sectors.
Effective transition to the state of being a digital-champion also requires a company to make important early decisions often targeted at legacy factors that would otherwise inhibit change. Those decisions include establishing a strong leadership position, engaging an appropriately skilled workforce, removing silo-based barriers, instituting cultural change in the corporate mindset and addressing ways of working throughout the organisation.
This article marks the first in our Digital Change for Infrastructure series.
This article marks the first in our Digital Change for Infrastructure series.
Sign up to receive future insights to your inbox.
Find out how Curzon Consulting can help your business
Related articles
Nothing found.
CONTACT US TO FIND OUT HOW WE CAN HELP
Patient experience: the case for home dialysis
We have just completed a major assessment of hospital, satellite and home dialysis delivery models.
Home dialysis: a cost effective solution that improves quality of life
We reviewed the efficacy and cost models associated with hospital, satellite and home dialysis models in multiple countries. In conclusion, whilst it’s not a one size fits all solution, home dialysis is a clear winner for the majority of people on dialysis.
Not only is a home dialysis solution 30-60% more cost effective over hospital and satellite models, it allows patients to perform dialysis in the comfort of their own home, significantly improving quality of life. No longer do patients have to visit a hospital or satellite centre 3 times per week/4-5 hours a session (incl. avg. commute time).
In addition, patients at home can perform nocturnal dialysis, which allows them to maintain a normal working life, which it itself results in wider benefits to the individual and society.
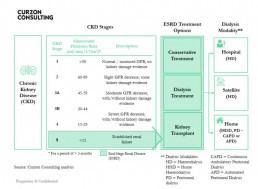
What is Chronic Kidney Disease?
- There are 5 stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Stage 5 is classified as end stage renal disease and is when a patient requires renal replacement therapy (transplant or dialysis)
- The Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) measures the amount of blood that passes through the tiny filters (glomeruli) in the kidneys, each minute
- The National Service Framework for Renal Services defies normal renal function as estimated GFR = />90 ml/min/1,73M2
- As Chronic Kidney disease (CKD) progresses the GFR falls
- Patients in ESRD have three treatment options:
1) Conservative Treatment – manage symptoms of kidney failure via lifestyle changes
2) Dialysis Treatment – conduct haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis
3) Kidney Transplant – replace kidney; more cost effective over 10 years than dialysis, but shortage of donors, means dialysis segment will grow - Patients who commence dialysis can have their treatment at a hospital, satellite (standalone clinic) or home
- Haemodialysis and Peritoneal dialysis have similar long-term survival rates
How prevalent is Chronic Kidney Disease in England?
- In England, there are an estimated 2.8m diagnosed and undiagnosed people (6.1%) of the population (>16 years old) that are thought to have CKD (Stage 3-5).
- In 2018, total population in England was ~56m, of which, >16 years old accounted for 45.4m (81%)
- CKD affects ~2.8m people over the age of 16. An estimated ~60,000 patients have End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD), of which, ~30,000 are on dialysis
- Prevalence rates are rising, largely due to better detection (2.4% in 2007, 4.3% in 2010 and 6.1% in 2017), poor nutrition and lifestyles, which is likely to cause pressure on health budgets
- Prevalence of chronic kidney disease stage 3-5 is expected to increase to 3.2m people by 2021 and 4.2m by 2036
- There are ~40,000 premature deaths every year due to chronic kidney disease (that’s enough people to fill the Royal Albert Hall nine times over)
- Chronic kidney disease diminished quality of life for many people and represents a significant financial burden on the NHS
- Black, Asian and minority ethnic communities are five times more likely to develop chronic kidney disease than other groups
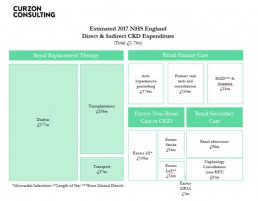
What are the costs of Chronic Kidney Disease in England?
- NHS England spends £1.7bn per annum on CKD (more than the combined £1.4bn cost to treat breast, lung, colon and skin cancer)
- Patients with CKD are likely to develop other health conditions, namely Hypertension, Stroke and/or Myocardial Infarction, resulting in adjacent costs in other non renal areas
- Mean annual direct cost of Dialysis care per patient is estimated to be £577m/30,000 = £19,233
- Full reimbursement by NHS and free at point of care
Source: Public Health England, CKD Prevalence Estimates published in 2014; Chronic Kidney Disease in England – The Human and Financial Cost; Curzon Consulting analysis
Annual dialysis cost by modality (hospital, satellite and home)
Home dialysis solution is not for all patients. Based on our analysis, when home dialysis is utilised, it can cost up to 40-60% lower than dialysis performed in hospitals and 30-40% lower when compared with satellite clinics
The total annual cost of delivering APD and CAPD is substantially lower than that for HD.
Studies in Belgium, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, UK and USA also found home-based modalities to be more cost effective.
In some countries, two patients can be treated on CAPD versus HD.
Despite overwhelming clinical and commercial evidence, home-based dialysis remains a small segment.
Payment models drive perverse incentives and therefore influence modality selection.
Find out how we can help you to design and implement this solution
If you’d like to learn how to design and implement an evidence-based home dialysis proposition, which can significantly reduce cost and transform patient quality of life, please get in touch.
We can help you to design and implement an evidence-based home dialysis proposition, which can significantly reduce cost and transform patient quality of life.
About the author

Chetan Trivedi
I lead Healthcare at Curzon Consulting.
For over 15 years I have supported Healthcare payers, providers and medical devices companies on strategy, operational improvement and digital transformation engagements across the UK, wider Europe, Middle East, US, India and Canada.
I am deeply passionate about improving health outcomes, safety and quality of life for patients.
CONTACT US TO FIND OUT HOW WE CAN HELP
Mobile stroke units - a stroke management study
Curzon Healthcare lead Chetan Trivedi has just completed an extensive study of Mobile Stroke Units (MSUs) in Australia, Argentina, Canada, Germany, Norway and the United States of America.
Our study included a detailed review of the efficacy of stroke management solutions, including the impact on economic and social costs downstream. We have also performed a detailed assessment of people, process and technology required to implement such solutions in other countries. Whilst our example shared below is focused on the UAE, a MSU can be implemented by any health system.
By adopting a Mobile Stroke Unit model, a health system can increase stroke survival rates, reduce disabilities and optimise the associated economic and social cost of care for stroke survivors through drastically decreasing “alarm-to-scan” and “scan-to-treatment” times.
Given our extensive intellectual capital (research and analysis) on the topic, we are able to develop a high-level business case within a few weeks for a local, regional or national health system.
Opportunity to Revolutionise Stroke Management in United Arab Emirates
By adopting a Mobile Stroke Unit (MSU) model, the UAE can increase stroke survival rates, reduce disabilities and optimise the associated economic and social cost of care for stroke survivors through drastically decreasing “alarm-to-scan” and “scan-to-treatment” times.
1. Situation
- There are two key types of stroke: ischemic and haemorrhagic
- Globally, ischemic stroke is the most common, occurring 85% of the time; but whilst haemorrhagic strokes only occur 15% of the time, they are responsible for 40% of deaths
- In the UAE, stroke is the third leading cause of death – “10,000 people suffer from stroke… every year”
- Stroke is the “number one cause of disability” – with only “10% of victims reaching a hospital on time to make a full recovery”
- Stroke “is estimated to cost the UAE around AED 3 billion per year, with additional cost to the economy of a further AED 4 billon in lost productivity, disability and informal care”
- The UAE had no stroke units in 2014 versus 12 in 2019, which is a major step in the right direction
- “The average age of occurrence of stroke is 45 in UAE which is much lower than the world age of 60 years”
Stroke is a major problem for health systems
2. Complication
- 2,000,000 brain cells/ neurons are lost every minute after a stroke, which translates to “Time is Brain”
- The earlier the stroke patient is diagnosed and treated, the better the patient outcomes, leading to a significant reduction in total cost of treating the patient over the life of their associated disabilities
Typical traditional model for stroke treatment is:
- Patient transported via ambulance into Accident & Emergency (A&E) or a specialist stroke unit
- Type of stroke determined by CT scan (a stroke patient cannot be treated until the type of stroke is determined)
- Treatment is administered based on stroke type (ischemic and haemorrhagic)
Through-out the entire process (from acute symptom onset to treatment), significant time is lost, which results in higher mortality risk and additional complications downstream
Correct diagnosis and time to treatment is crucial
3. Question
Despite great progress made in stroke intervention in the UAE in recent times, what can the UAE do to deliver transformative change to increase post stroke survival rates, reduce disabilities associated with stroke, improve patient quality of life post stroke and reduce the associated economic burden on the stroke patient, their family and wider society?
4. Solution
- Instead of patients being transported to A&E or a specialist Stroke Unit, losing valuable time, a specialist Mobile Stroke Unit (MSU) can travel to the patient to deliver emergency point-of-care diagnosis and treatment onsite
- The Mobile Stroke Unit solution was pioneered in Germany back in 2011 and such solutions are being delivered in Australia, Argentina, Canada, Germany, Norway and the US
Key Mobile Stroke Unit attributes typically include:
- appropriately trained emergency response team (e.g. driver, paramedic, critical care nurse and CT technician, optional Vascular Neurologist)
- a Computerized Tomography (CT) scanner
- a point-of-care laboratory system (e.g., serum sodium, potassium, chloride, ionized calcium, total CO2, glucose, etc.)
- a telehealth solution, where a Vascular Neurologist and Pharmacist can video call into the Ambulance to provide guidance to the paramedic team
- an Artificial Intelligence solution to provide on-site diagnosis to rule out stroke-like symptoms (e.g. migraines, seizures, Bells Palsy, inner ear problems etc.), which may not be related to stroke
The most important benefit of the Mobile Stroke Unit is rapid diagnosis of the stroke type and treatment with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) can be started more rapidly if appropriate
A randomised controlled trial shows, treatment with Intravenous TPA can be started within an average of 38 minutes when patients are treated in an Mobile Stroke Unit compared with 73 minutes under the existing model
Evidence shows on-site stroke treatment improves patient outcomes
Source:
https://www.stroke.org/understand-stroke/what-is-stroke/hemorrhagic-stroke/; The Epidemiology of Stroke in the Middle East, El-Jha et al 2016; https://www.arabhealthonline.com/magazine/en/latest-issue/2019-show-issue/mechanical-thrombectomy-for-acute-ischaemic-stroke-in-uae.html; The mobile stroke unit and management of acute stroke in rural settings, Shuaib and Terakihi 2018; https://gulfnews.com/uae/health/know-the-signs-of-a-stroke-and-where-to-get-help-1.65494094; Curzon Consulting analysis